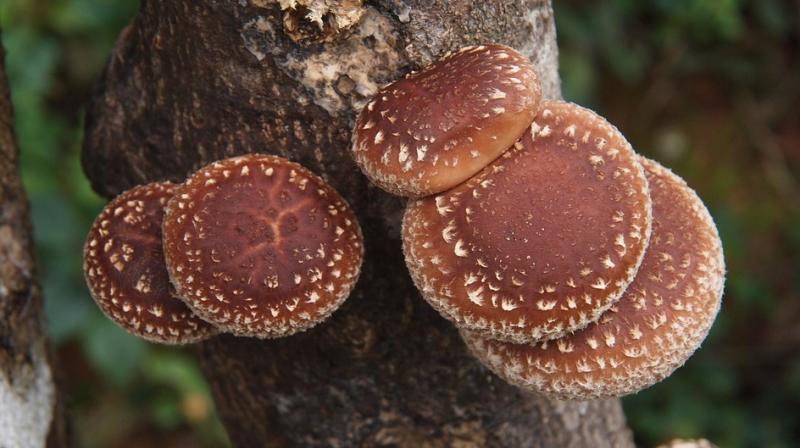
In Germany a 50-year-old man went to hospital with the rash a few days after attending an Asian food festival. Some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can cause a similar reaction, but doctors diagnosed him with shiitake flagellate dermatitis – caused by eating raw shiitake mushrooms.
The shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) is a popular Asian food and represents the second most consumed mushroom in the world. It is known for having a range of strong health benefits including antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. Especially in Asia, this mushroom has been used in patients with cancers of the gastrointestinal tract and also may be helpful in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus. The source of these effects is lentinan, a polysaccharide in the mushroom.
Shiitake dermatitis, also known as flagellate dermatitis due to the whip-like marks, was first identified in 1977 by a Japanese scientist who saw several patients with the reaction after eating the mushroom. Since this seminal report, numerous cases (England, France, USA) have followed. This disorder is mainly seen in Asia.
The symptoms are caused by a toxic reaction to a molecule called lentinan. This breaks down upon heating, which is why only raw or partially cooked shiitake mushrooms cause a problem. The rash, which is often itchy with red spots and small blisters that form in a whip-like line on the torso, arms and legs, usually begins to appear within 2-3 days of eating the mushroom and lasts anything from ten to 21 days. Steroids may be used to shorten the duration of the rash, and antihistamines given for the itch.
It’s important that ost cases of shiitake dermatitis reportedly have resulted from eating raw or partially cooked mushrooms. Therefore, it is important to fully cook the mushrooms before consuming. Frying, or boiling the shiitake mushrooms removes the risk of rash. According the statistics only 2% or less of the population is likely to be affected and then only if they consume raw or undercooked shiitake.
Some workers in shiitake grow houses develop an eczema-like rash due to shiitake specific immunoglobulin. There are also documented cases of allergic and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by spores of shiitake. This type of pneumonitis also identified according to other mushroom species.